22 missing after avalanche hits BRO project site
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 4)
| Topic: GS3 – Disaster – Disaster Management |
|
Context |
|
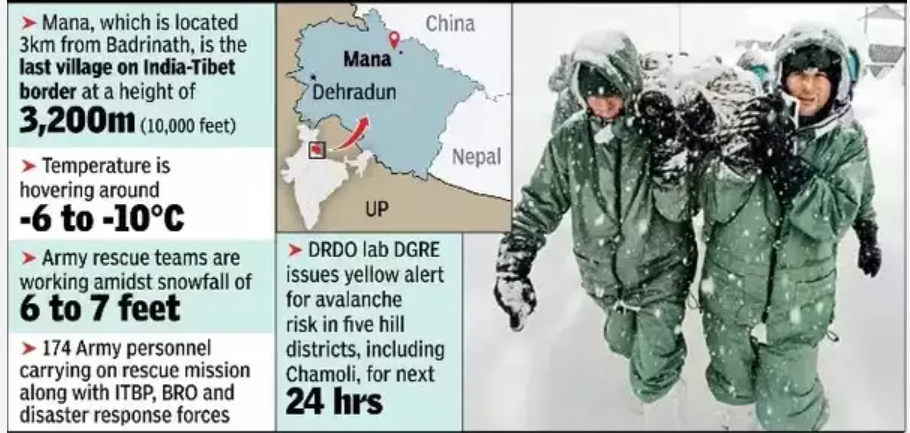
Causes of Glacier Avalanches:
Glacier avalanches occur due to a combination of natural and environmental factors. These include:
-
Heavy Snowfall and Ice Accumulation: Excessive snowfall increases the weight of glaciers, making them unstable.
-
Temperature Fluctuations: Rapid warming weakens ice structures, leading to cracks and eventual collapse.
-
Seismic Activity: Earthquakes and tremors can trigger ice breakages, causing large avalanches.
-
Glacial Meltwater: Water from melting glaciers reduces friction, making ice more prone to sliding.
-
Climate Change: Rising global temperatures accelerate glacial melting and increase avalanche risks.
-
Steep Slopes and Gravity: Glaciers on steep terrains are naturally prone to collapse under their weight.
Ways to Prevent Glacier Avalanches
-
Early Warning Systems: Implementing satellite and sensor-based monitoring to detect glacial movements.
-
Controlled Blasting: Triggering small avalanches in a controlled manner to prevent massive collapses.
-
Reducing Climate Change Impact: Cutting carbon emissions to slow global warming and glacial melting.
-
Restricting Construction: Avoiding infrastructure projects in high-risk avalanche-prone zones.
-
Snow Barriers and Retention Structures: Building walls and barriers to stabilize slopes.
-
Public Awareness and Training: Educating locals and workers about avalanche risks and emergency responses.
-
Improved Forecasting: Using meteorological data to predict heavy snowfall and potential avalanche conditions.
|
Practice Question: How can glacier avalanche risks be mitigated in high-altitude regions? Suggest scientific and policy measures to reduce their impact. (150 Words /10 marks) |

