
Disaster Management Free UPSC Notes Download

Disasters and Natural Hazards
A Disaster is an undesirable occurrence resulting from forces that are largely outside human control, strike quickly with little or no warning, and cause or threaten serious disruption of life and property including death and injury to a large number of people

Disaster Management in India
It is the sovereign responsibility of the state to protect the citizens from disasters. In the Indian federal system, the responsibility for disaster management is that of the state government. The central government mainly works for the coordination of disaster management

Global Efforts for Disaster Management
Global efforts for disaster management emerged as the world recognized the need for sustainable development.
The 1972 Stockholm Conference

Environmental Impact Assessment
Environmental Impact Assessment is a process whereby people’s views are taken into consideration for granting final approval to any developmental project or activity.

Coastal Regulation Zones
Under the Environmental Protection Act 1986, notification was issued in 1991 for regulation of activities in the coastal area by MoEF. It defined the Coastal Regulation Zone (CRZ)

Earthquakes
Earthquakes are shaking of the earth caused by to sudden release of energy. Massive Natural earthquakes are generally caused by the energy released due to Movement in tectonic plates

Tsunami
Tsunami: Large sea waves caused by sudden displacement of ocean water due to Earthquakes and volcanic eruptions. that cause the sea floor to move abruptly resulting in the form of high vertical waves called Tsunamis
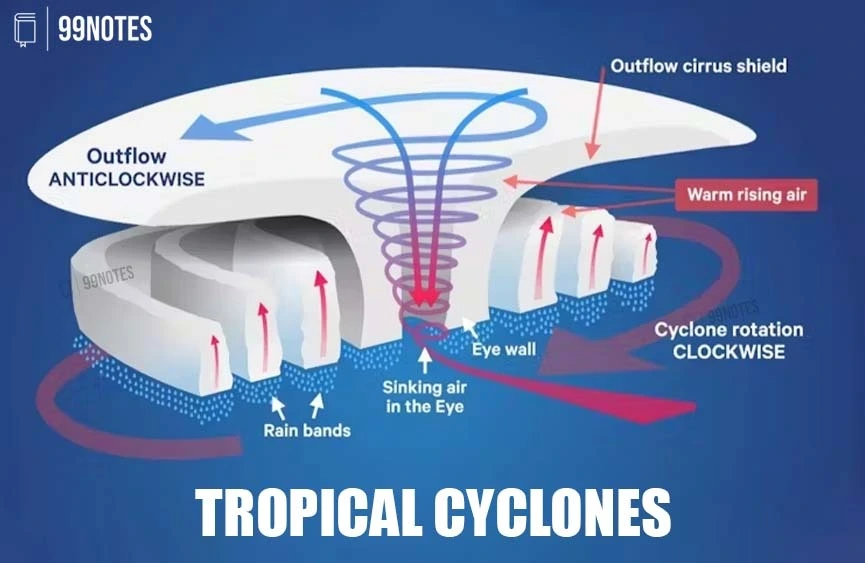
Tropical Cyclones
Tropical cyclones (or hurricanes) are intense low-pressure areas confined to the area lying between 30° N and 30° S latitudes, in the atmosphere around which high-velocity winds blow

Floods
When Surface run-off exceeds the carrying capacity of the river channels, streams, lakes and other inland water in which they flow bodies or the infiltration rate of the ground we call it a Flood.

Droughts
Droughts are an extended period when there is a shortage of water availability due to inadequate precipitation, excessive rate of evaporation and over-utilisation of water from the reservoirs and other storages, including the groundwater.

Heat Wave
Qualitatively, a heat wave is a condition of air temperature that becomes fatal to the human body when exposed. This generally comes as a heatstroke. Quantitatively, it is defined based on the temperature thresholds over a region in terms of actual temperature
Landslide Avalanches and Mud-flows
In this chapter, we aim to study all types of mass movements which are hazardous to human life and livelihood. These include landslides, Avalanches, rockfalls, Mud-flow and earth flows
Disaster Management
Disasters are events that cause widespread damage, loss, or suffering, and disaster management refers to the processes and systems in place to prepare for, respond to, and recover from disasters.
Disaster management involves a range of activities, including risk assessment, preparedness planning, response and recovery operations, and reconstruction.
There are several types of disasters that can occur, including natural disasters, such as earthquakes, hurricanes, and floods, and man-made disasters, such as oil spills, terrorist attacks, and technological failures.
- Risk assessment is an important part of disaster management, and it involves identifying the hazards that could potentially cause a disaster, analyzing the likelihood and consequences of these hazards, and evaluating the effectiveness of measures in place to reduce the risk. This information can be used to develop preparedness plans and to identify the resources and capabilities that will be needed in the event of a disaster.
- Preparedness planning involves creating a plan of action to follow in the event of a disaster, as well as organizing resources and establishing protocols for communication and coordination. This can include measures such as training emergency responders, developing evacuation plans, and stocking emergency supplies.
- Response and recovery operations are the actions taken to address the immediate impacts of a disaster and to restore essential services. This can include search and rescue efforts, providing emergency shelter and supplies, and restoring power and communications.
- Reconstruction involves rebuilding and repairing the damage caused by a disaster, as well as implementing measures to reduce the risk of future disasters. This can include rebuilding infrastructure, such as roads and buildings, and implementing land use and building codes to make communities more resilient to future disasters.
- Disaster management is typically the responsibility of governments, but it can also involve the participation of non-governmental organizations, international organizations, and the private sector. Effective disaster management requires coordination and cooperation among these different stakeholders.
There are several principles of disaster management that guide the response to disasters, including:
- The precautionary principle: This principle states that action should be taken to prevent or mitigate the potential negative consequences of a disaster, even in the absence of complete scientific certainty.
- The principle of prevention: This principle emphasizes the importance of preventing disasters from occurring, rather than simply responding to their effects.
- The principle of preparedness: This principle emphasizes the importance of being prepared for disasters and having the necessary resources and capabilities in place to respond effectively.
- The principle of participation: This principle recognizes the importance of involving all stakeholders, including affected communities, in the planning and implementation of disaster management activities.
- The principle of coordination: This principle emphasizes the importance of coordinating the efforts of different stakeholders in the response to a disaster.
- The principle of transparency: This principle requires that disaster management activities be conducted in an open and transparent manner, with information being shared openly with all stakeholders.
- The principle of accountability: This principle requires that those involved in disaster management be held accountable for their actions and that they be transparent in their decision-making processes.
Disaster management is a complex and multifaceted field, and it requires a comprehensive and integrated approach to be effective. It is important to consider not only the immediate impacts of a disaster, but also the long-term consequences and the potential for future disasters.
Other Topics Related to Environment:

