Basic Science Free UPSC Notes Download

Cells
Cells form the basic unit of structure and function in living organisms. They perform vital biological processes like metabolism, growth, and reproduction. The study of cells helps explain how life operates at the microscopic level, influencing all fields of biology and medicine.

Reproduction
Reproduction is the biological process by which living organisms produce offspring to ensure species survival. It occurs in two main forms: sexual and asexual reproduction, each involving different mechanisms of genetic transfer and diversity.

Reproduction in Humans
Reproduction in humans is a sexual process involving the fusion of male and female gametes. It encompasses fertilization, embryonic development, and birth, supported by specialized reproductive organs and hormonal regulation.
Tissues
Tissues are groups of similar cells that perform a specific function in an organism, forming the structural and functional foundation of organs. In multicellular organisms, tissues are broadly classified into plant and animal tissues. Understanding their types and roles is essential in biology and biotechnology applications.
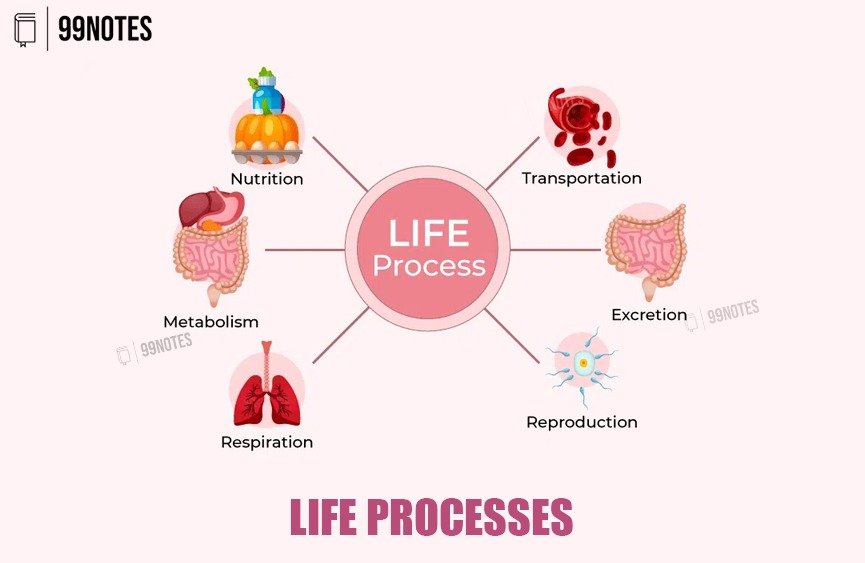
Life-Processes
Life processes are essential biological functions that maintain life in organisms, such as respiration, nutrition, transportation, and excretion. These processes enable growth, reproduction, and survival.

Control and Coordination
The nervous system and endocrine system work together to control and coordinate bodily activities. They help organisms sense changes, transmit signals, and trigger suitable actions for survival and stability.

Introduction to Classical Physics
Classical physics focuses on the laws describing the behavior of matter and energy at everyday scales. It includes Newtonian mechanics, heat, light, and electricity, establishing the groundwork for modern scientific advancements.

Units and Measurement
Measurement involves quantifying physical properties using standardized units. Units and measurement are crucial for comparison, calculation, and communication in science, ensuring precise and reliable results.

Mechanics
Mechanics deals with the behavior of physical bodies under forces. It includes the analysis of motion and the forces causing it, forming the foundation of classical physics and engineering.
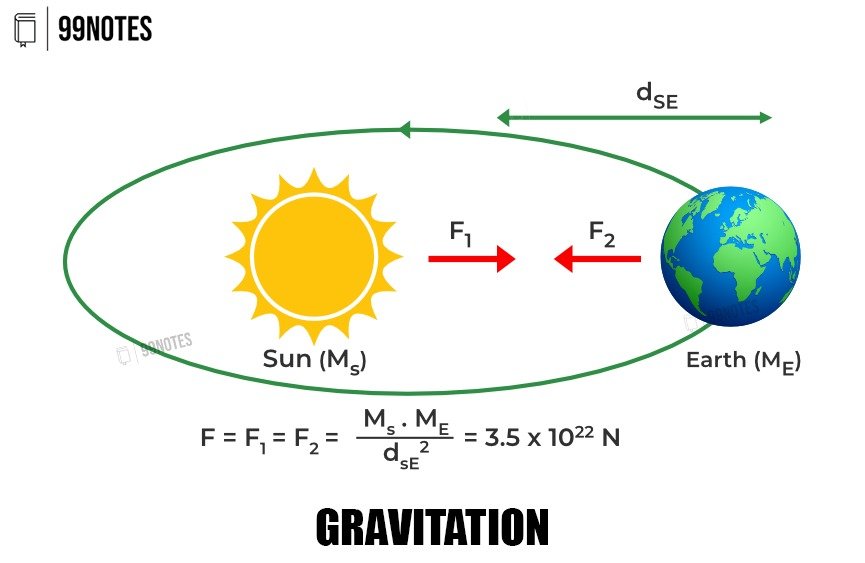
Gravitation
Gravitation is the universal force of attraction between masses. It governs planetary orbits, ocean tides, and the fall of objects, and is described by Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation.
Vibrations and Waves
Vibrations refer to periodic motions, while waves are the propagation of these oscillations through space or matter. Understanding vibrations and waves is key to studying sound, light, and other physical phenomena.

Electromagnetic Waves
Electromagnetic waves propagate energy without a medium, combining electric and magnetic fields. They cover a broad spectrum from low-frequency radio waves to high-frequency gamma rays, integral to communication and medical technologies.
Light
Light consists of electromagnetic radiation within a certain wavelength range. It travels in straight lines and interacts with materials through reflection, refraction, and absorption, fundamental to optics and imaging.

Thermodynamics
Thermodynamics helps us understand the efficiency of machines, energy conservation, and entropy. Its principles are applied in industries, space research, and everyday appliances.

Mechanical Properties of Fluids
Mechanical properties of fluids describe how liquids and gases respond to forces. Key concepts include pressure, viscosity, buoyancy, and surface tension, influencing natural phenomena and engineering applications.
Electricity
Electricity is the flow of electric charge through conductors. This topic includes current, resistance, Ohm’s law, and circuit elements, forming the basis of electrical engineering and technology.
Einstein’s Relativity
Relativity theory, proposed by Einstein, describes how motion affects time and space perception. Special Relativity deals with uniform motion, while General Relativity explains gravity as space-time curvature.

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
Radiation and matter show wave-particle duality, displaying characteristics of both waves and particles depending on the situation. This duality is fundamental in modern physics and quantum theory.

Atom
Atoms are tiny particles that form the building blocks of everything around us. Understanding their composition and behavior is crucial for physics, chemistry, and nuclear science.
Nuclei
Electromagnetic waves propagate energy without a medium, combining electric and magnetic fields. They cover a broad spectrum from low-frequency radio waves to high-frequency gamma rays, integral to communication and medical technologies.
- Basic Science Free UPSC Notes Download
- Cells
- Reproduction
- Reproduction in Humans
- Tissues
- Life-Processes
- Control and Coordination
- Introduction to Classical Physics
- Units and Measurement
- Mechanics
- Gravitation
- Vibrations and Waves
- Electromagnetic Waves
- Light
- Thermodynamics
- Mechanical Properties of Fluids
- Electricity
- Einstein's Relativity
- Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
- Atom
- Nuclei
- Other Related Links:
