Waqf (Amendment) Bill 2024
(Source – Indian Express, Section – Explained, Page – 16)
| Topic: GS2 – Polity |
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
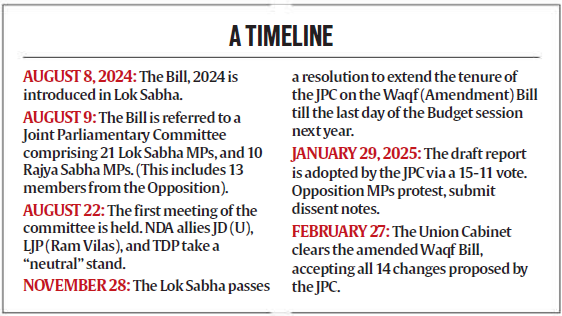
What is a Waqf Property?
- A Waqf is a property donated by Muslims for a specific religious, charitable, or private purpose. Ownership of the property is considered to belong to God, while its benefits are directed to the specified purposes.
- Establishment: A Waqf can be established through a written deed, legal instrument, or orally.
- Use and Permanence: A property may be recognized as Waqf if it has been used for religious or charitable purposes over an extended period. Once declared Waqf, the property’s status is permanent and irreversible.
Representation on Waqf Boards
- The Bill allows non-Muslims to be appointed as Chief Executive Officers and members of state waqf boards, which has sparked opposition.
- Critics argue that waqf is a religious matter and should be managed exclusively by Muslims.
- While the requirement for appointees to have knowledge of Muslim law was introduced as an amendment, the controversy persists over religious representation.
Government Control Over Waqf Property
- A key concern is the transfer of authority to determine waqf status from the Waqf Tribunal to a state government officer.
- Since this officer is part of the state administration, critics argue there is a conflict of interest, fearing that decisions may be biased in favor of the government when disputes arise.
Abolition of ‘Waqf by User’
- The Bill removes the concept of “waqf by user,” which allowed properties used for religious or charitable purposes over time to be recognized as waqf, even without formal documentation.
- This change could lead to disputes over existing mosques, graveyards, and other waqf properties lacking legal paperwork.
Mandatory Waqf Database Registration
- The Bill mandates that all waqf properties be registered in a central database within six months, failing which legal protections could be lost.
- While amendments allow the Waqf Tribunal to extend this deadline, the lack of clarity on eligibility for extensions raises concerns about potential property disputes and encroachments.
Changes in Waqf Tribunal Powers
- The composition of the Waqf Tribunal has been altered, now including a state government officer alongside a District Judge.
- Additionally, the Tribunal’s decisions are no longer final and can be challenged in High Courts, potentially leading to prolonged legal battles.
Conclusion
- The Waqf (Amendment) Bill, 2024, introduces structural changes that critics argue could weaken waqf institutions and increase government control.
- The concerns revolve around religious representation, legal safeguards for waqf properties, and the potential for increased litigation.
- The Bill’s impact will largely depend on its implementation and judicial scrutiny.
| Waqf Amendment Bill 2024 Significance |
|
The Waqf Amendment Bill 2024 is a significant legislative proposal aimed at modernizing and improving the management of Waqf properties in India. It is significant for the following reasons:
|
| Practice Question: The Waqf (Amendment) Bill, 2024 has sparked widespread criticism over its provisions related to waqf governance, property disputes, and judicial oversight. Critically analyze the key changes introduced by the Bill and their potential implications on religious and property rights in India. (250 Words /15 marks) |
