Easing food prices drive inflation down
|
| The News |
|
What is Inflation?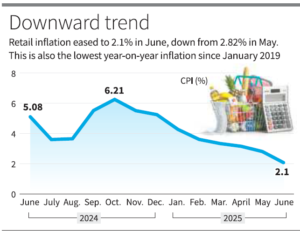
- Inflation refers to the rate at which the general level of prices for goods and services rises, leading to a decrease in the purchasing power of money.
- It occurs when too much money chases too few goods.
- In several recent months in a row, the inflation has remained down.
How is it measured?
CPI and WPI are two indices
- Consumer Price Index (CPI) is a measure that examines the inflation in the weighted average of prices of a basket of consumer goods and services, such as transportation, food, and medical care.
- Wholesale Price Index (WPI) is a measure that examines the inflation in the weighted average of prices of a basket of wholesale goods such as manufactured products, primary articles, and Energy (fuel and power).
CPI and WPI figures are released by the National Statistical Office (NSO), Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI) every month.
Categories of CPI
Types of CPI in India:
- CPI for Industrial Workers (IW)
- CPI for Agricultural Labourers (AL)
- CPI for Rural Labourers (RL)
- CPI for Rural, Urban, and Combined (used for inflation targeting).
| Category | Weight (%) |
| Food & Beverages | 45.86 |
| Pan, Tobacco, Intoxicants | 2.38 |
| Clothing & Footwear | 6.53 |
| Housing | 10.07 |
| Fuel & Light | 6.84 |
| Miscellaneous | 28.32 |
Understanding the News:
Low Fuel prices leading to lower food Inflation; it’s good for consumers, but might be bad for farmers.
- Within the CPI, the food and beverages category was the only major component to record a contraction, declining by 0.2% in June 2025, compared to an inflation rate of 8.4% in June 2024. This marks the eighth consecutive month of easing food inflation.
- In the WPI category, the food articles category saw prices contract by 3.75% in June 2025, compared to an inflation rate of 11.1% in June 2024. That’s huge.
- Another major contributor to easing wholesale prices was crude petroleum and natural gas, which contracted by 12.3% in June, marking the 10th consecutive month of decline, with the last three months registering double-digit contractions.
India targets CPI to measure inflation
Under the Monetary Policy Framework Agreement (2015) between the RBI and the Government of India:
- Inflation target: 4% CPI inflation with ±2% band (i.e., 2%–6%).
- This is mandated under the RBI Act, 1934 (amended in 2016).
Why do we target CPI instead of WPI?
CPI has been mutually agreed target by the RBI and the government for inflation targeting, but not WPI, because:
- Reflects retail prices: CPI represents the prices faced by consumers, aligning with the cost of living and welfare.
- Includes services: Services form a significant part of the economy and consumer expenditure.
- Direct impact on households: Monetary policy aims at consumer welfare and controlling the cost of living.
- WPI excludes services and doesn’t reflect consumer prices accurately.
- Domestic Prices: WPI is largely dependent on the prices of commodities that are determined by international markets.
