Tertiary and Quaternary Activities
TYPES OF TERTIARY ACTIVITIES
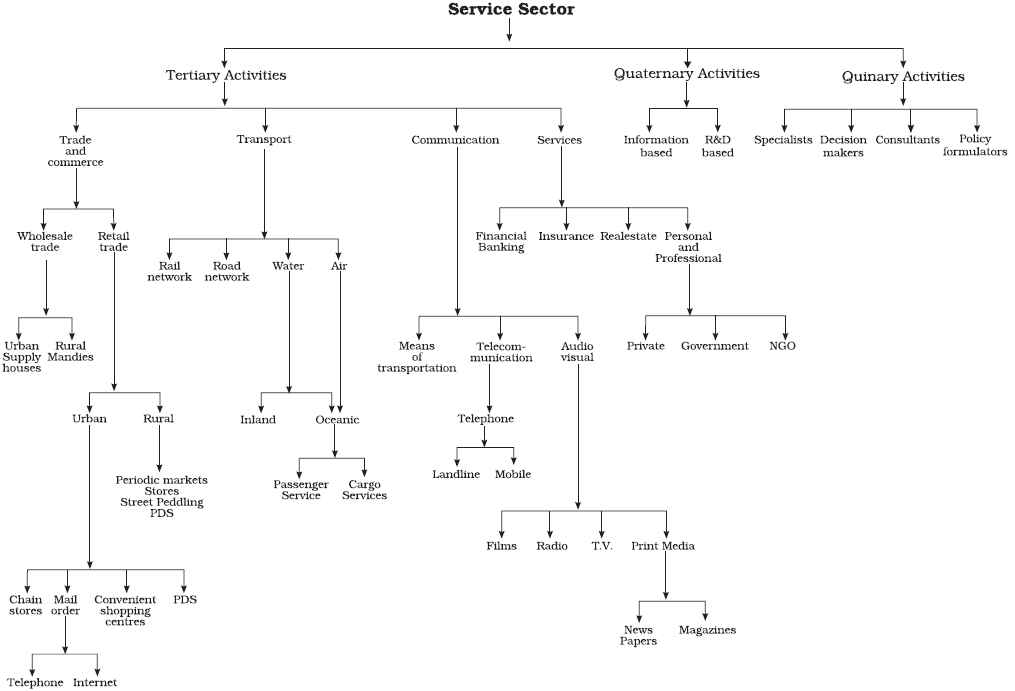
Trade and Commerce:
Buying and selling of items. Takes place at trading centres.
Divided into two types:
1.Rural marketing centres:
These are quasi-urban centres that serve as trading centres of the most rudimentary type. [Here one must recall that urban] Personal and professional services are not well-developed. These form local collecting and distributing centres.
- Wholesale Market: Most of these have mandis (wholesale markets) and also retailing areas. They are not urban centres per se (in themselves) but are significant centres for making available goods and services which are most frequently demanded by rural folk.
- Periodic Markets in rural areas: These may be weekly, bi-weekly markets from where people from surrounding areas meet their temporally accumulated demand. They are held on specified dates and move from one place to another.
2.Urban Market Centres:
Such centres provide ordinary goods and services as well as many of the specialised goods and services required by people; offer manufactured goods as well as many specialised markets developed, For example, markets for labour, housing, semi or finished products. Services of educational institutions and professionals such as teachers, lawyers, consultants, physicians, dentists and veterinary doctors are available.
- Retail Trading Services: Concerned with the sale of goods directly to the consumers. Most of the retail trading takes place in fixed establishments or stores solely devoted to selling. Street peddling, handcarts, trucks, door-to-door, mail-order, telephone, automatic vending machines and the internet are examples of non-store retail selling.
- Wholesale Trading Services: constitutes bulk business through numerous intermediary merchants and supply houses and not through retail stores. Some large stores including chain stores are able to buy directly from the manufacturers. However, most retail stores procure supplies from an intermediary source.
Wholesalers often extend credit to retail stores to such an extent that the retailer operates very largely on the wholesaler’s capital.
Transport and Communication Services:
Speedy and efficient transport systems are required to assist in the production, distribution and consumption of goods. At every stage in this complex system, the value of the material is significantly enhanced by transportation.
Distance is the most important factor in the transportation and communication services. It can be measured as:
- Length Cost or kilometre distance
- Time distance
- Cost distance: the expense of travelling.
Distance, in terms of time or cost, is the most important determining factor. Isochrone lines are drawn on a map to join places equal in terms of the time taken to reach them.
Factors Affecting Transport services:
- Demand: influenced by the size of the population.
- Routes: location of cities, towns, villages, industrial centres and raw materials,
- The pattern of existing trade between them,
- Natural factors: nature of the landscape between them, type of climate, and
- Funds are available for overcoming obstacles along the length of the route.
Communication services
Transmission of messages was initially carried by hand, animals, boats, roads, rail and air; In today’s world communication has become instantaneous.
Types of communications today.
- Print Media: For example, Newspaper.
- Telecommunications: linked to the development of electrical technology. It has revolutionised communications because of the speed – time reduced from weeks to minutes and recent advancements like mobile telephony have made communications direct and instantaneous at any time and from anywhere. The telegraph, morse code and telex have almost become things of the past.
- Radio and Television: Relay news, pictures, and audio to audiences around the world: Mass Media.
- Satellite communication: Relay information all around the globe.
Services:
In economics, a service is an intangible act or an intangible utility for which a consumer pays. Most people today are service workers; In developed countries, there are more in numbers than in developing countries. For example, in the USA more than 75% of people are engaged in services.
Characteristics of Services:
The two most important characteristics of service are:
- Immaterial exchange of value occurs – i.e. it is just like any other economic activity.
- It is provided to individual consumers who can afford to pay for them.
Classification of services:
- Low-order services, such as grocery shops and laundries, are more common and widespread than high-order services.
- High-order services or more specialised ones like those of accountants, consultants and physicians.
- Formal sector services: Many services have been regulated: For example, making highways and bridges, customer care, and educational services are supervised or performed by the government or companies. Legislation has established corporations to supervise and control the marketing of such services.
- Informal/non-formal sector services: Personal services are made available to the people to facilitate their work in daily life. Workers migrate from rural areas in search of employment and are unskilled. They are employed in domestic services as housekeepers, cooks, and gardeners. This segment of workers is unorganised.
Important Service sectors
Tourism:
Tourism is undertaken for the purpose of recreation. It is the world’s largest tertiary activity – in total 250 million registered jobs and total revenue (40% of total GDP). Many local persons are employed to provide services: accommodations, meals, transport, entertainment and special shops. It fosters the growth of infrastructure industries, retail trading, and craft industries.
Tourist regions: Warmer places around the Mediterranean Coast and West coast of India, Winter sports regions, found mainly in mountainous areas, and various scenic landscapes and national parks, which are scattered. Historic towns also attract tourists.
Factors affecting tourism:
- Demand: rapidly increased in the last century, with improvement in the standard of living
- Transport: Opening up of tourist areas – aided by improvement in transport facilities.
- Tourist attractions: Its marketing and infrastructure such as museums etc.
- Climate: Most people from colder regions expect to have warm, sunny weather for beach holidays.: Southern Europe and Mediterranean – offers almost consistently higher temperatures, than in other parts of Europe, long hours of sunshine and low rainfall throughout the peak season. OR seek snow cover suitable for skiing.
- Landscape: An attractive environment: Mountains, lakes, spectacular sea coasts and landscapes not completely altered by man.
- History and Art: potential attractiveness; Ancient or picturesque towns and archaeological sites, castles, palaces and churches.
- Culture and Economy: Attract tourists with a penchant for experiencing ethnic and local customs. If a region provides for the needs of tourists at a cheap cost – it is likely to become very popular.
QUARTERNARY SECTOR:
The quaternary sector works in a segment of the service sector that is knowledge-oriented. This sector can be divided into quaternary and quinary activities.
Quaternary activities involve some of the following: the collection, production and dissemination of information or even the production of information.
Entrepreneurs:
Entrepreneurs are Empowered workers of the Quarternary sector and slowly emerging Quinary sector.
They represent an important stage of development in the hierarchy of economic activity where the need for self-actualisation is not motivated by wealth and security alone but by other factors. They have predominantly a value system that emphasises quality of life and believes in creativity and individual values.
Various Quaternary sector services
It centres around research, and development and may be seen as an advanced form of service involving specialised knowledge, technical skills, and administrative competence.
Over half of all workers in developed economies are in the ‘Knowledge Sector’ and there has been a very high growth in demand for and consumption of information-based services.
- Financial information services: For example, Mutual fund manager,
- IT: software developers and statisticians; Who create information-based products.
- Personnel working in office buildings, elementary schools, university classrooms, hospital and doctors’ offices, theatres, accounting and brokerage firms: all belong to this category.
QUINARY SERVICES:
These are the highest level of decision-makers or policymakers who perform quinary activities. These are subtly different from the knowledge-based industries that the quinary sector in general deals with.
They focus on the creation, re-arrangement and interpretation of new and existing ideas; data interpretation and the use and evaluation of new technologies.
These are often referred to as ‘gold collar’ professions, they represent another subdivision of the tertiary sector representing special and highly paid skills of senior business executives, government officials, research scientists, financial and legal consultants, etc.
Their importance in the structure of advanced economies far outweighs their numbers.
Outsourcing:
The process of contracting out is giving work to an outside agency to improve efficiency and reduce costs – has resulted in the opening up of a large number of call centres in India, China, Eastern Europe, Israel, the Philippines and Costa Rica – due to cheap and skilled workers. These are also out-migrating countries. Outsourcing countries face resistance from job-seeking youths.
Business processes being outsourced: information technology (IT), human resources, customer support and call centre services and at times also manufacturing and engineering.
New Outsourcing trends in the Quinary sector:
- Knowledge processing outsourcing (KPO): It is distinct from business Process Outsourcing (BPO) as it involves more high skilled workers. It is information-driven knowledge outsourcing. KPO enables companies to create additional business opportunities.
- Examples: research and development (R and D) activities, e-learning, business research, intellectual property (IP) research, the legal profession and the banking sector.
- Homeshoring: the practice of transferring employment that was previously carried out in a company’s office or factory to employees’ homes. It is an alternative to outsourcing.
- Business process outsourcing (BPO), is a business practice in which one organization hires another company to perform a process task that the hiring organization requires for its own business to operate successfully.
- Medical Services for Overseas patients: Medical Tourism: About 2L patients come to India annually for treatment. India has emerged as the world leader. Chennai – caters to 45% of all businesses.
- Medical tourism brings abundant benefits to developing countries like India, Thailand, Singapore and Malaysia.
- Another trend: is outsourcing of medical tests and data interpretation. Hospitals in India, Switzerland and Australia have been performing certain medical services – ranging from reading radiology images, to interpreting Magnetic Resonance Images (MRIs) and ultrasound tests.
There is immense potential in the Service sector in India, since it requires little investment part from investment in education, and has great margins. Further, it is the future of the world. However, the Digital divide between areas Urban and rural areas in ICT access paves the biggest challenge against development in this sector.
Related FAQs of Tertiary and Quaternary Activities
Tertiary activities are services that help connect producers and consumers. These include trade, transport, communication, education, healthcare, and more. They don’t produce goods—but they’re vital for economic flow!
Trade is split into rural and urban market centres. Rural centres like mandis and weekly markets cater to local needs, while urban markets offer a wider variety—like labour markets, retail stores, and even professional services.
Retail trading sells goods directly to consumers—think local shops or even online stores. Wholesale trading is more B2B, where goods are sold in bulk to retailers or other intermediaries.
Quaternary services deal with knowledge—like IT, education, R&D. Quinary services are high-level decision-making roles like CEOs, scientists, and policymakers. Think of it as brainpower driving the economy!
Outsourcing—especially BPOs and KPOs—has boomed in India due to our skilled, English-speaking workforce. It helps global companies reduce costs, and boosts jobs here in fields like IT, legal, finance, and even healthcare.



